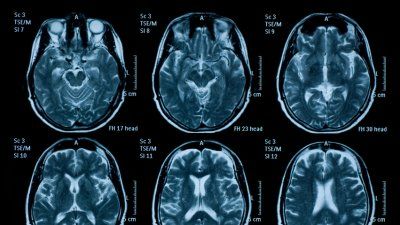
Study Points to Immune System’s Role in Neural Development
A new study shows that an immune signal named interleukin 33 plays a crucial role in allowing the brain to maintain the optimal number of synapses during the development of the central nervous system.