University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSF-
-
After 10-Year Search, Scientists Find Second ‘Short Sleep’ Gene
UCSF scientists who identified the only human gene known to promote “natural short sleep” have discovered a second.

-
Most long-term acute care hospital patients die within five years
-
UCSF Gets New Money to Study the ‘Galaxies’ Within You (Your Microbes)
-
Elderly Have Poor Prognosis After Recovery in Long-Term Acute Care Hospitals
While long-term acute care hospitals are designed to help patients recover and regain independence, fewer than 1-in-5 older adults who were transferred to such facilities were alive five years later.

-
Study Questions Mainstay Treatment For Mild Asthma
-
Study Finds New Blood Test Could Help Detect Brain Injury In Minutes
-
Simple Blood Test Unmasks Concussions Absent on CT Scans
Blood test that is currently under development may flag concussion in CT-negative patients, enabling them to be evaluated for long-term complications.

-
Living With HIV
-
Chemical Exposure Web Tool Defines Risks Faced by Millions of California Women
A new web tool spells out for the first time the exposures that more than 6.5 million working women in California face that could increase their risk for breast cancer, including industrial solvents, antimicrobials and phthalates.

-
Tobacco Vs. E-Cigarette Use Differs Among SF Public Schools
Eighty-eight percent of the e-cigarette waste collected was found at schools serving predominantly upper-income families with mostly white student populations. None were found at schools serving predominantly low- and middle-income families with large Latinx and African American populations.

-
Why Warning Pregnant Women Not to Drink Can Backfire
-
Scorpion Toxin That Targets ‘Wasabi Receptor’ May Help Solve Mystery of Chronic Pain
Researchers discovered a scorpion toxin that targets the “wasabi receptor,” which they think it can be used as a tool for studying chronic pain and inflammation, and may eventually lead to the development of new kinds of non-opioid pain relievers.

-
Students Who Are First in Their Family to Attend College Share Stories, Experiences
Nearly one-third of the students at UCSF are the first in their families to graduate from college. They shared stories of finding mentorship, struggling with self-doubt, and paving the way for others.

-
Increasing Blood Pressure Medications at Hospital Discharge May Pose Serious Risk
Increasing medications for blood pressure when discharging older patients from the hospital may pose a greater risk of falls, fainting and acute kidney injury that outweighs the potential benefits.
-
Upping Seniors' Blood Pressure Meds After Hospital Can Sometimes Bring Danger
-
New Clues on Stem Cell Transplant Rejection Revealed in Study
Study shows that the adult-to-iPSC conversion process can mutate DNA found in mitochondria, causing mice and humans to reject iPSCs, and stem cell transplants more generally.
-
Moisturizers May Be Turning Your Skin Into ‘Swiss Cheese’
Researchers want to learn how to repair certain types of skin rather than providing short-term relief.
-
Tweaked CRISPR in Neurons Gives Scientists New Power to Probe Brain Diseases
In a paper researchers describe a technique that uses a special version of CRISPR developed at UCSF to systematically alter the activity of genes in human neurons generated from stem cells, the first successful merger of stem cell-derived cell types and CRISPR screening technologies.
-
UCSF making sure breastfeeding mothers get the help they need
-
Pregnant moms who breathe dirty air have children with lower IQs, study finds
-
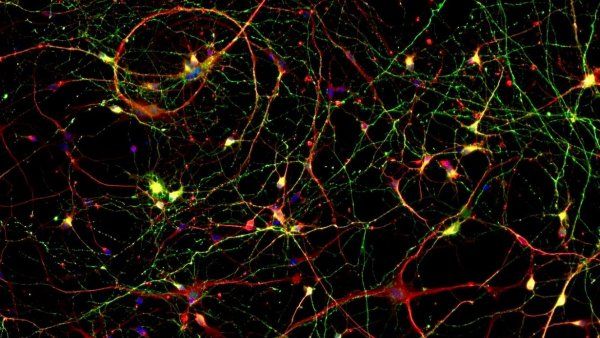
Molecular Recycling in the Brain May Keep Alzheimer’s at Bay
Scientists identify faulty molecular recycling as potential driver of Alzheimer’s disease.
-
The Morning-est Morning People
-
Marc and Lynne Benioff Donate $35M to UCSF, Stanford to Advance Microbiome Science
The gifts will launch new research initiatives on their respective campuses to leverage the growing science of the human microbiome.
-
Gift Launches New UCSF Benioff Center for Microbiome Medicine
UCSF researchers aim to radically rethink the role of the microbiome in early life and develop new interventions aimed at preventing childhood diseases.

-
UCSF Names Pediatrics Chair, Physician-in-Chief for Benioff Children’s Hospitals
Raphael Hirsch comes to UCSF from the University of Iowa Carver College of Medicine, where he served as chair of the Stead Family Department of Pediatrics.

-
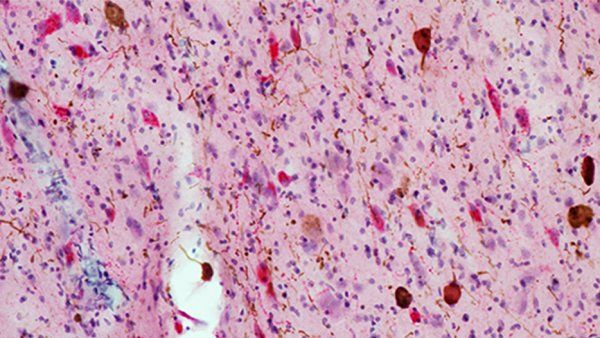
Alzheimer’s Disease Destroys Neurons that Keep Us Awake
UCSF scientists show that Alzheimer’s disease directly attacks brain regions responsible for wakefulness during the day.
-
Is Your Sleep Cycle Out of Sync? It May Be Genetic
-
UC Faculty Demands Elsevier Restart Negotiations
A group of prominent University of California faculty say they will step away from the editorial boards of scientific journals published by Elsevier until the publishing giant agrees to restart negotiations.

-
Genome Study Reveals Clues to Komodo Dragon’s Unique Abilities