University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSF-
-
UCSF finds major clue to the cause of sudden-onset paralysis in children
-
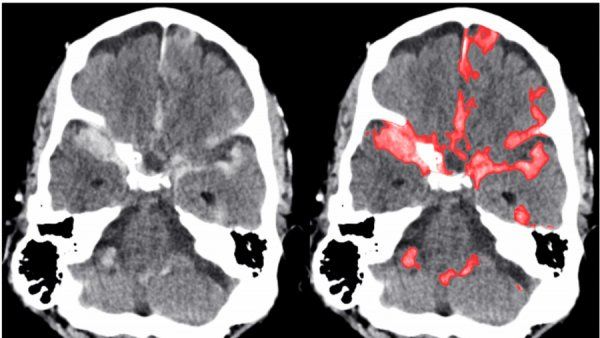
AI Rivals Expert Radiologists at Detecting Brain Hemorrhages
An algorithm developed by scientists at UC San Francisco and UC Berkeley did better than two out of four expert radiologists at finding tiny brain hemorrhages in head scans—an advance that one day may help doctors treat patients with TBI, strokes and aneurysms.
-
‘Missing’ Virus Detected in Dozens of Children Paralyzed by Polio-Like Illness
Research team has detected the immunological remnants of a common seasonal virus in spinal fluid from dozens of patients diagnosed with acute flaccid myelitis (AFM). The findings provide the clearest evidence to date that AFM is caused by an enterovirus (EV) that invades and impairs the central nervous system.

-
NIH-Funded Research Consortium to Target Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration
The National Institutes of Health has awarded a five-year, multi-investigator research grant expected to total more than $63 million to Mayo Clinic and UC San Francisco, to advance treatments for frontotemporal lobar degeneration.
-
Dementia Spreads via Connected Brain Networks
Scientists used maps of brain connections to predict how brain atrophy would spread in individual patients with frontotemporal dementia, adding to growing evidence that the loss of brain cells associated with dementia spreads via the synaptic connections between established brain networks.

-
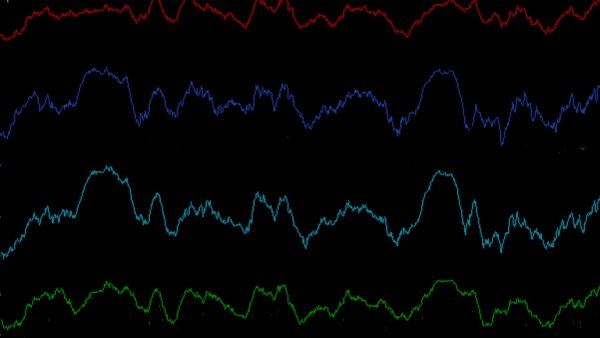
Key to Learning and Forgetting Identified in Sleeping Brain
Distinct patterns of electrical activity in the sleeping brain may influence whether we remember or forget what we learned the previous day.
-
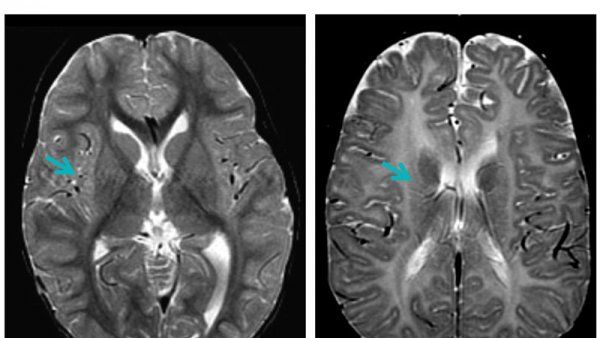
Stem Cell Studies Offer Hope for Childhood Neurological Condition
International team of researchers report progress in using stem cells to develop new therapies for Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, a rare genetic condition affecting boys that can be fatal before 10 years of age.
-
New Study: Veterans at greater risk for Dementia and Alzheimer’s
-
Study Finds New Blood Test Could Help Detect Brain Injury In Minutes
-
Simple Blood Test Unmasks Concussions Absent on CT Scans
Blood test that is currently under development may flag concussion in CT-negative patients, enabling them to be evaluated for long-term complications.

-
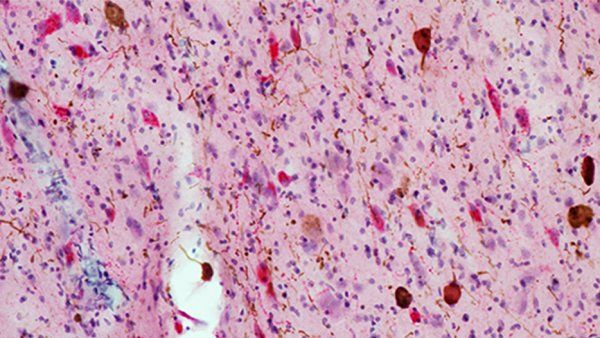
Alzheimer’s Disease Destroys Neurons that Keep Us Awake
UCSF scientists show that Alzheimer’s disease directly attacks brain regions responsible for wakefulness during the day.
-
Team IDs Spoken Words and Phrases in Real Time from Brain’s Speech Signals
UCSF scientists have for the first time decoded spoken words and phrases in real time from the brain signals that control speech.

-
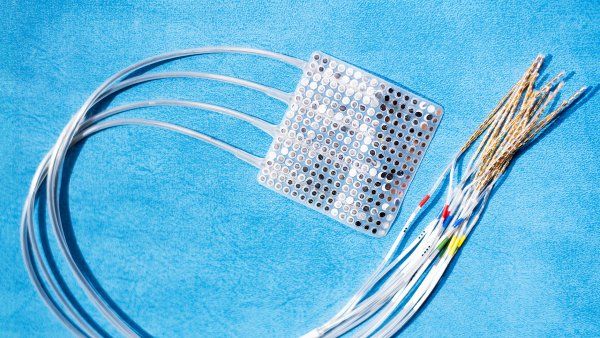
Unraveling the Ethics of New Neurotechnologies
Since 2017, UCSF researchers Winston Chiong and Eddie Chang have led a collaborative neuroethics research project funded by the NIH.
-
Multiple Sclerosis Attacks Brain’s ‘Projection Neurons’
Brain damage associated with MS specifically targets a common class of brain cells called projection neurons
-
Scientists Discover Autoimmune Disease Associated with Testicular Cancer
Using advanced technology, scientists have discovered an autoimmune disease that appears to affect men with testicular cancer.
-
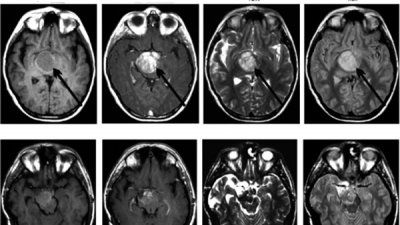
A Decade of Research Sharpens View of Brain Tumor Genetics, Causes
Today, our understanding of glioma subtypes has expanded to include the molecular and genetic variants that can influence a tumor’s development, prognosis, and response to treatment.
-
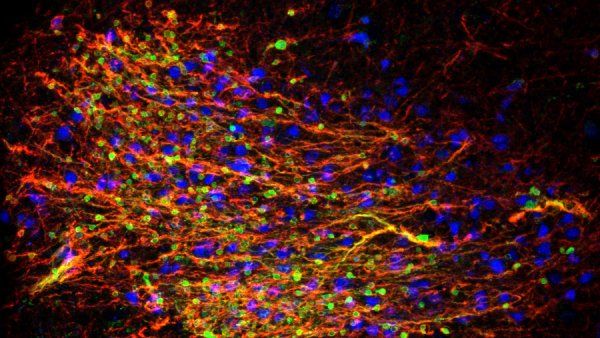
Mood Neurons Mature During Adolescence
A new study suggests that the human brain may maintain reserves of immature neurons throughout life, using these “Peter Pan” cells in a similar manner to the neurogenesis seen in other species
-
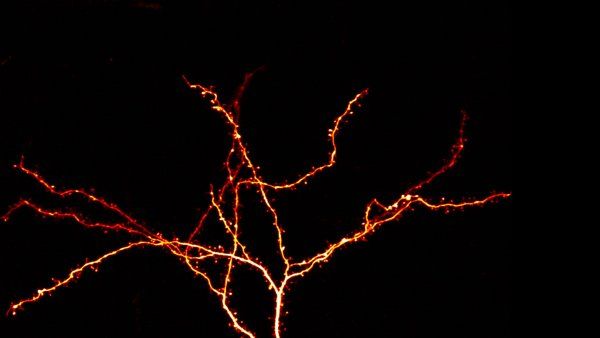
Key Gene Mutation in Autism May Alter Brain in Early Years of Life
Unlike other gene mutations linked to autism, which are thought to alter brain development before birth, the newly identified changes in brain signaling may occur closer to the onset of autism symptoms in the first years of life.
-
Algorithm that Tailors Digital Meditation Program Improves Attention and Memory
The intervention, an app called MediTrain, uses a closed-loop algorithm that tailors the length of meditation sessions to the abilities of the participants.

-
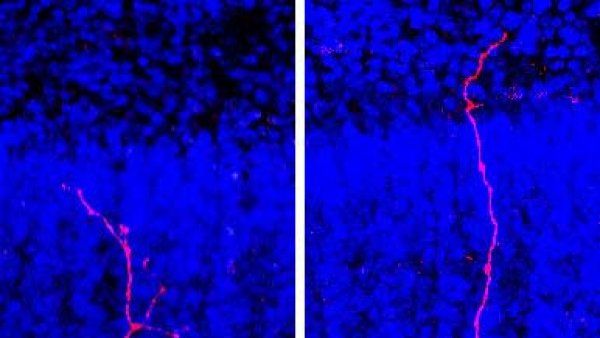
Brain Changes in Autism Traced to Specific Cell Types
Changes in gene activity in specific brain cells are associated with the severity of autism in children and young adults with the disorder.
-
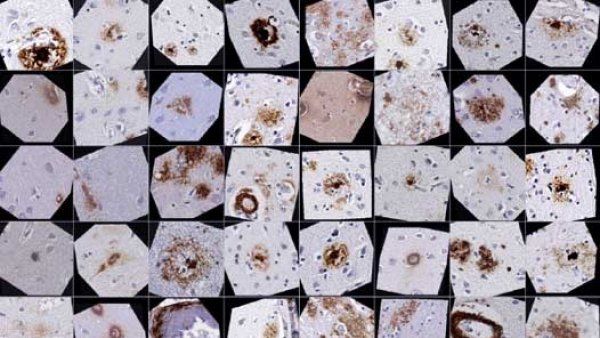
Artificial Intelligence Could Vastly Scale Up Alzheimer’s Research
Researchers have found a way to teach a computer to precisely detect one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease in human brain tissue.
-
These Scientists Want to Redefine Alzheimer's as a 'Double-Prion' Disease
-
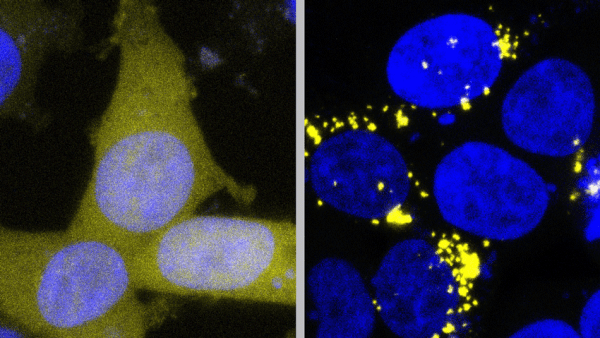
Alzheimer’s Disease is a ‘Double-Prion Disorder,’ Study Shows
Two proteins central to the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease act as prions – spreading through tissue like an infection by forcing normal proteins to adopt the same misfolded shape.
-
I Have ALS, I wish a polygenic analysis had told me it was coming
-
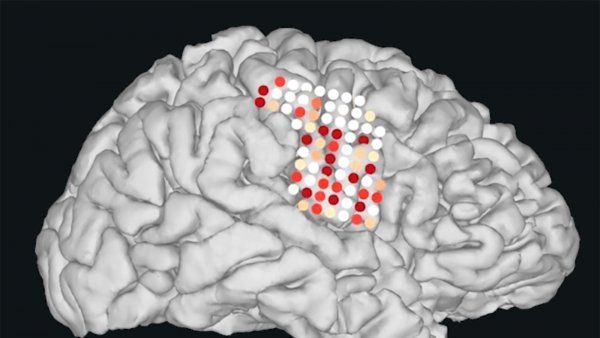
Synthetic Speech Generated from Brain Recordings
The technology could one day restore the voices of people who have lost the ability to speak due to paralysis and other forms of neurological damage.
-
Scientists Turn Brain Signals Into Speech, May Help People Who Cannot Talk
-
What Does It Mean to Spell Check Your Genetic Code?
-
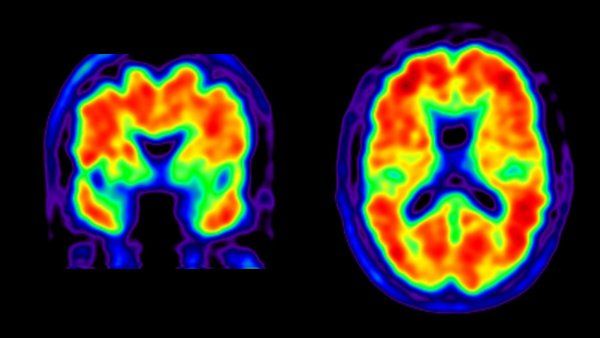
Brain Scans Spot, Track Alzheimer's
-
Alzheimer’s Diagnosis, Management Improved by Brain Scans
Amyloid positive PET scan. A first-of-its-kind national study has found that a form of brain imaging that detects Alzheimer’s-related “plaques” significantly influenced clinical management of