Novel Surgical Technique Paves Way to Restoring Failing Organs
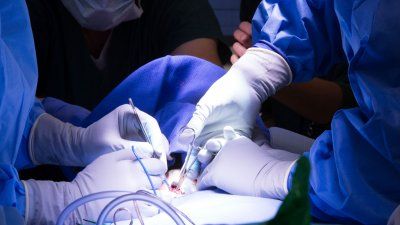
By piercing liver cells with rapid pulses of electricity, scientists at UC San Francisco have demonstrated an entirely new way to transplant cells into organs to treat disease.
University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSFBy piercing liver cells with rapid pulses of electricity, scientists at UC San Francisco have demonstrated an entirely new way to transplant cells into organs to treat disease.

How T cells feel out intruders rapidly and reliably enough to nip infections and other threats in the bud has remained a mystery to researchers.
A test commonly used in breast cancer has been found to also identify which patients with aggressive prostate cancer will benefit from hormonal therapy.
Of the nearly 6,000 physician mothers in the survey, nearly 78 percent reported discrimination of any type.

Researchers at UCSF and their colleagues have found that Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection among people who inject drugs remains high and stable in some North American cities but incidence has dropped and remained low in some Australian and European cities.

Researchers made a significant advance, identifying the first “high-confidence” risk gene for Tourette disorder as well as three other probable risk genes.
UCSF researchers are looking to the front teeth of mice to to help understand how stem cells know when it’s time for them to expand in numbers and transform into mature, adult cells in order to renew injured or aging tissue.

Children’s exposure to racial and ethnic discrimination has been linked to their likelihood of having asthma in a new study by UCSF researchers.

UCSF researcher Grant Dorsey received federal funding for the Program for Resistance, Immunology, Surveillance and Modeling of Malaria in Uganda.

Research shows that the lungs secrete a specialized enzyme capable of destroying chitin, without which chitin particles inhaled from the environment can accumulate in the airways and trigger inflammatory lung disease.
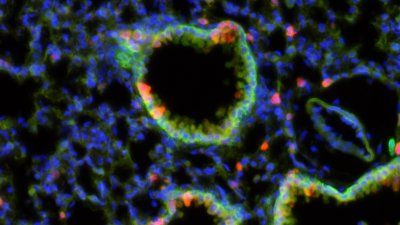
Young adults get more pleasure from smoking cigarettes while they are drinking alcohol than they do while using marijuana, according to a new UC San Francisco study.

Women enrolled in California’s Medicaid program (Medi-Cal) who have been diagnosed with severe mental illness have been screened for cervical cancer at much lower rates than other women.

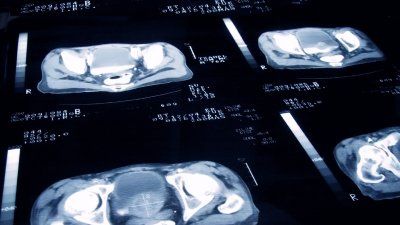
A new study led by UC San Francisco has found that radiation doses can be safely and effectively reduced – and more consistently administered – for common CT scans.

In a major advance for fundamental biological research, UCSF scientists have developed a tool capable of illuminating previously inscrutable cellular signaling networks.

After undergoing surgery, elderly patients often experience cloudy thinking. Mounting evidence suggests that heightened inflammation in the brain following surgery is the more likely cause.

A video game under development as a medical device boosts attention in some children with sensory processing dysfunction.

Researchers at UCSF and elsewhere are turning to virtual experiments for the initial steps of drug development.

Americans of South Asian descent are twice as likely as whites to have risks for heart disease, stroke and diabetes, when their weight is in the normal range.
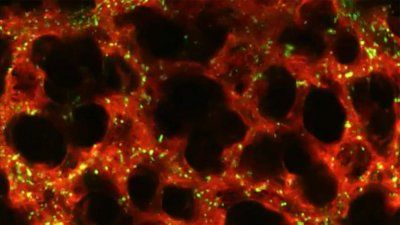
Smoking by either parent helps promote genetic deletions in children that are associated with the development and progression of the most common type of childhood cancer, according to research headed by UCSF.

UCSF researchers have used data-mining computational tools to identify a treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma, a cancer associated with underlying liver disease and cirrhosis that often only becomes symptomatic when it is very advanced.
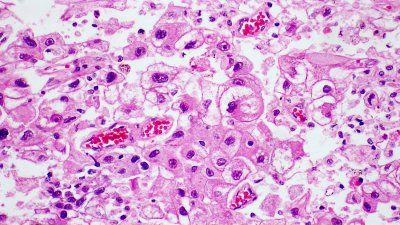
A newly approved drug that is the first to reflect the current scientific understanding of multiple sclerosis is holding new hope for the hundreds of thousands Americans living with the disease. It also highlights the importance of clinician scientists like UCSF’s Stephen Hauser who are working to transform research into cures for patients.

An innovative virtual glucose management service for hospitalized patients with diabetes is highly effective at maintaining appropriate glucose levels.

UCSF researchers have helped to identify the three evolutionary steps the polio virus used to evolve from harmless vaccine into a regional menace. With the new knowledge, they have developed a new polio vaccine that should be unable to escape and cause outbreaks.

UCSF was the top public recipient of biomedical research grants from the National Institutes of Health or the sixth consecutive year in 2016, and the second-highest recipient among all public and private institutions nationwide.

Learn more about some of the UCSF researchers who received the top funding from the National Institutes of Health in 2016.

UCSF has worked strategically with community partners in the SFHIP to enact high-impact policies, such as banning sugar-sweetened beverages from hospitals, to improve public health and reduce health inequities in the city.

Using video microscopy in the living mouse lung, UC San Francisco scientists have revealed that the lungs play a previously unrecognized role in blood production.
Location-tracking apps on smartphones could be used to help track and manage care for thousands of patients who suffer from chronic diseases, and possibly provide feedback to them on lifestyle changes.

Researcher Annesa Flentje is looking at ways stress among sexual minorities – those whose sexual orientation, identity or practices differ from the majority – can affect physical and mental health, starting at the genetic level, with a particular focus of late on the effect of stress on HIV-positive men.
