Drug Reverses Memory Failure Caused by Traumatic Brain Injury
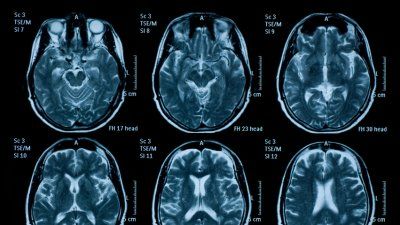
UCSF scientists used an experimental drug to completely reverse severe learning and memory impairments caused by traumatic brain injury in mice.
University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSFUCSF scientists used an experimental drug to completely reverse severe learning and memory impairments caused by traumatic brain injury in mice.

Google search volume across the United States could help fill in the gaps on cancer incidence and mortality data, according to a new study by scientists at UCSF and the University of Pennsylvania.

Youth-rated films, which are designed and marketed as kid-friendly, continue to fill the movie screen with tobacco imagery.

Immune cells in the brain trigger overeating and weight gain in response to diets rich in fat, according to a new study in mice led by researchers from UCSF and the UW Medical Center.

UCSF scientists have mapped in exquisite detail a protein complex called NOMPC, which acts as a mechanoreceptor in animals from fruit flies to fish and frogs.

Twenty-six UCSF investigators received funding from the 2017 cycle of the Marcus Program in Precision Medicine Innovation to help generate understanding of human disease.
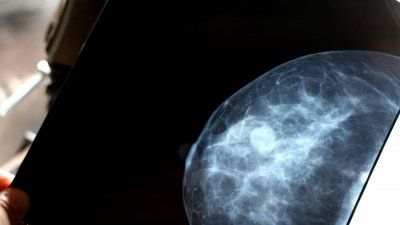
A molecular test can pinpoint which patients will have a very low risk of death from breast cancer even 20 years after diagnosis and tumor removal, according to a new clinical study led by UCSF in collaboration with colleagues in Sweden.
Liberal consumption of so-called good fats – like those found in olive oil and avocados – may lead to fatty liver disease, a risk factor for metabolic disorders like type 2 diabetes and hypertension, according to a new study by scientists at UCSF.

Specialized cells in the gut sense potentially noxious chemicals and trigger electrical impulses in nearby nerve fibers, according to a new study led by UCSF scientists.

Crowdsourcing for health and medical research leads to certain groups being either over- or underrepresented by age, race/ethnicity, education and physical activity, according to a UCSF-led study.

When we purchase something, there's often an assumption that it's safe. Unfortunately, many prevalently used chemicals could cause serious effects on health, especially during prenatal development.

A new study by UCSF researchers revealed the intriguing possibility that HP1α binds to stretches of DNA and pulls it into droplets that shield the genetic material inside from the molecular machinery of the nucleus that reads and translates the genome.

Around one in five children with Tourette syndrome, a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary movements and vocalizations, met criteria for autism in a study headed by UCSF.

Community-based interventions for HIV testing and treatment in rural East Africa nearly doubled rates of HIV viral suppression over two years, according to a study by UC San Francisco researchers.

Researchers need access to multiple strains of marijuana in order to find out about its potential benefits or harms, but current legislation makes that extremely difficult. As states move ahead with recreational legalization, access is more critical than ever.

Asian-American women are more likely to experience delays in follow-up treatment after an abnormal mammogram compared to white women, according to new UCSF research.

Racial discrimination experienced by African-American children and young adults exacerbates a type of asthma known to be resistant to standard treatment, according to a study headed by researchers at UCSF.

Organoids serve as dioramas of disease, allowing UCSF scientists to understand how and why problems occur during tissue development. It's also a small step toward the creation of full-sized organs we could use for transplant.

Black heart attack patients suffer higher mortality rates than white patients when ambulances are diverted because hospital emergency rooms are too busy to receive new patients.

Researchers at UCSF have found that older people with persistent pain show quicker declines in memory as they age and are more likely to have dementia years later.

Bicycle use has skyrocketed in popularity, but it’s also led to more accidents, with medical costs from non-fatal bike crashes climbing steadily by $789 million annually, according to a new study by UCSF.

Cancer specialists from UCSF will present new findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO), the world’s largest clinical cancer research meeting.

UCSF researchers have drawn a link between genetic abnormalities in neurodegenerative diseases and the formation of RNA foci, work the scientists said may open avenues to the development of new drug treatments.

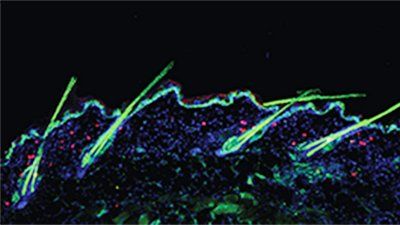
In experiments in mice, UC San Francisco researchers have discovered that regulatory T cells, directly trigger stem cells in the skin to promote healthy hair growth.
A user-friendly website and advance directive form given directly to patients can be highly effective in empowering older adults to plan for their future medical care.

Providing healthy women with information about pelvic examinations, including a professional society’s strong recommendation against them, substantially decreases the patients’ desire for the exam.

Colon cancer patients who have a healthy body weight, exercise regularly and eat a diet high in whole grains, fruits and vegetables have a significantly lower risk of cancer recurrence or death.

Postmenopausal women who reached menopause at an earlier age or who never gave birth may be at higher risk for heart disease, according to a new study by researchers at UCSF Health.
