Weaning Triggers Metabolic Shift That is Reversed in Diabetes
Examination of human tissue samples suggested that T2D may represent a reversion to a more infant-like metabolic state.

University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSFExamination of human tissue samples suggested that T2D may represent a reversion to a more infant-like metabolic state.

A major 2009 revision to a federal nutrition program for low-income pregnant women and children improved recipients’ health on several key measures.

State policies requiring children to attend additional years of school may result in a reduced risk for heart disease and improvements in several cardiovascular risk factors in adulthood.

A new study suggests that the human brain may maintain reserves of immature neurons throughout life, using these “Peter Pan” cells in a similar manner to the neurogenesis seen in other species
Unlike other gene mutations linked to autism, which are thought to alter brain development before birth, the newly identified changes in brain signaling may occur closer to the onset of autism symptoms in the first years of life.
Adolescents who see themselves as puny and who exercise to gain weight may be at risk of so-called muscularity-oriented disordered eating behaviors.

A new study from UCSF suggests that a protein found in the common bullfrog may one day be used to detect and neutralize a poisonous compound produced by red tides and other harmful algal blooms.

Women who were denied abortions reported higher rates of joint pain, persistent headaches and migraines, and poorer overall health five years later, compared to women able to obtain abortions.

Excessive napping may be an early warning sign of age-related cognitive decline in older men, according to a 12-year study by UC San Francisco scientists.

Research identifies enzymes produced by two different bacterial species that work together to digest L-Dopa in the human gut. Blocking one of these bacterial enzymes could significantly boost the drug’s efficacy in these patients.

The Laboratory for Genomic Research represents a novel hybrid model that brings together industrial and academic researchers under a single roof working on projects both together and independently.

An international study may offer hope to people with a rare and debilitating genetic disorder, PKAN, as well as a potentially new approach to treat other neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis.

Pioneering test called metagenomic next-generation sequencing shown to identify infections better than any standard clinical method.
A two-week course of an experimental immunotherapy called teplizumab dramatically reduced type 1 diabetes (T1D) diagnosis rates in people at high risk for the disease, according to newly published

The program, supported by philanthropists Herb and Marion Sandler, funds ideas that challenge generally-accepted theories and have potentially transformative effects.

Consuming high levels of red meat or white poultry resulted in higher blood cholesterol levels than consuming a comparable amount of plant proteins.

A study has lodged a new kink in the breastfeeding dilemma that adds to the angst of exhausted new parents: While most newborns lose weight in the first days of life, do you or don’t you offer a

The intervention, an app called MediTrain, uses a closed-loop algorithm that tailors the length of meditation sessions to the abilities of the participants.

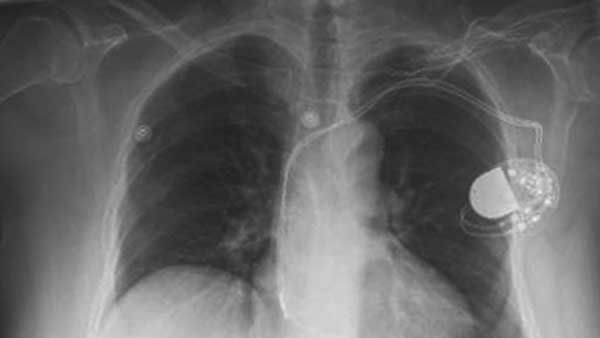
Blood-pressure and glucose control may be effective in preventing heart block, a common form of arrhythmia, and the subsequent need for a pacemaker.
The UCSF study examined whether a mobile phone physical activity app combined with brief, in-person counseling increased and maintained levels of physical activity

A renewed push by several states to restrict access to abortions could have negative consequences for the health and well-being of women, as well as their children, research has shown.

A research team led by scientists at UC San Francisco and the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub has developed a new CRISPR-based diagnostic tool, dubbed FLASH, that can rapidly identify any drug-resistant