University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSF-
-
Breastfeeding May Bring Added Bonus for Women With MS
-
The Startling Secret of an Invincible Virus
-
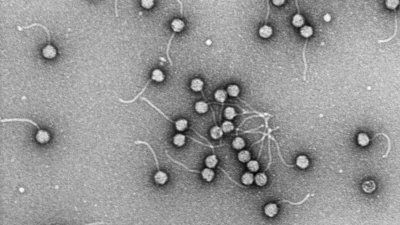
CRISPR-Resistant Viruses Build ‘Safe Rooms’ to Shield Genomes from DNA-Dicing Enzymes
After phages infect bacteria, they construct an impenetrable “safe room” inside of their host, which protects vulnerable phage DNA from antiviral enzymes. This compartment, which resembles a cell nucleus, is the most effective CRISPR shield ever discovered in viruses.
-
Woman’s e-cigarette habit leads to her 'cobalt lung' diagnosis – an incurable disease found only in metal workers
-
How a Single Blood Test May Provide a ‘Head-to-Toe’ Health Check
UCSF physician Peter Ganz and colleagues at Colorado-based SomaLogic Inc., are developing what they call “liquid health check” technology – a single blood test capable of painting a detailed portrait of a person’s current health and future disease risks.

-
Ahead of Supreme Court Hearing, Researchers Say Abortion Law Will Harm Women’s Health
The brief surveys evidence from more than 20 studies on the safety of abortion, the harms of denying women abortions when they seek them, and what happens when abortion providers are required to obtain admitting privileges.

-
How Overexcited Neurons Might Affect How You Age
-
Experts Say Solutions to Homelessness Known, Require Commitment
-
Deportation fears linked to high blood pressure among immigrant women
-
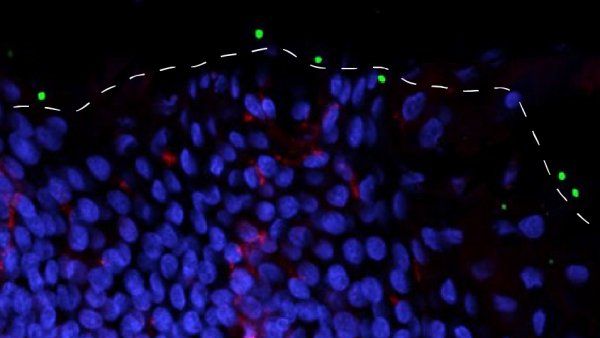
Newborn Immune System Detects Harmful Skin Bacteria
UCSF scientists found that an early-life window of immune tolerance available to a normally harmless bacterial species is firmly closed to another, often pathogenic species — one that is a leading cause of drug-resistant skin infections in the U.S. and occasional source of “flesh-eating” necrosis.
-
This Doctor Wants to Use Salesforce Blockchain to Cut Cancer Drug Development Costs in Half
-
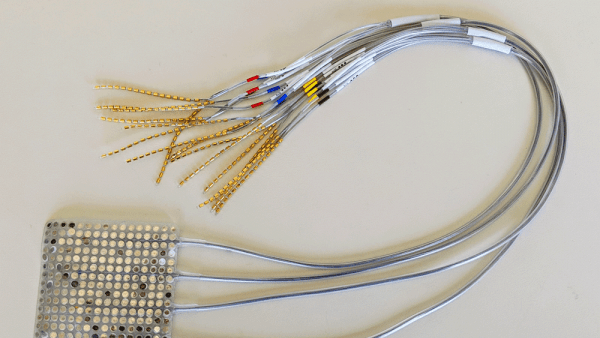
How the Brain Detects the Rhythms of Speech
Neuroscientists discovered how the listening brain scans speech to break it down into syllables. The findings provide for the first time a neural basis for the fundamental atoms of language and insights into our perception of the rhythmic poetry of speech.
-
The Loudness Of Vowels Helps The Brain Break Down Speech Into Syl-La-Bles
-
Will Science Ever Give Us a Better Night’s Sleep?
-
Many Patients with Anorexia Nervosa Get Better, But Complete Recovery Elusive to Most
Three in four patients with anorexia nervosa make a partial recovery. But just 21 percent make a full recovery, a milestone that is most likely to signal permanent remission.

-
Amid vape epidemic, Marin researcher sheds light on e-cigarette waste
-
‘Supergrowth’ Challenges Established Science of Cell Growth
Research shows that after cells are subjected to certain stressful treatments, they appear to gain a new “superpower” that allows them to grow twice as fast as normal — a feature the authors call “supergrowth.”
-
In Down Syndrome Mouse Model, Scientists Reverse Intellectual Deficits with Drugs
Using standard animal model of Down syndrome, scientists were able to correct the learning and memory deficits associated with the condition with drugs that target the body’s response to cellular stresses.
-
We Know We’re Full Because Intestine’s Stretch Sensors Tell Us So
We commonly think a full stomach is what tells us to stop eating, but it may be that a stretched intestine plays an even bigger role in making us feel sated.
-
Researchers Halt Spread of Breast Cancer by Blocking Metastasis-Promoting Enzyme
In a breakthrough with important implications for the future of immunotherapy for breast cancer, UCSF scientists have found that blocking the activity of a single enzyme can prevent a common type of breast cancer from spreading to distant organs.

-
Conflict of Interest Statements Don’t Affect Peer Review
New study reveals that peer reviewers do not take conflicts of interest disclosures into account in their recommendations to journal editors, likely because of an absence of clear guidelines on how conflicts should impact their evaluations.

-
Weill Neurohub Will Unite UCSF, UC Berkeley, U. of Washington to Find New Treatments for Brain Diseases
With a $106 million gift from the Weill Family Foundation, UC Berkeley, UC San Francisco, and the University of Washington have launched the Weill Neurohub to speed the development of new therapies for diseases and disorders that affect the brain and nervous system.
-
Sandy and Joan Weill donate $106M for brain research at UCSF, UC Berkeley, UW
-
The Science Is Extremely Clear: You Need to Prioritize Sleep
-
New York’s Jails Are Failing. Is the Answer 3,600 Miles Away?
-
Pregnant people are being offered an unproven treatment to “reverse” abortions
-
‘Basket’ Trials for Dementia Aim to Bring Precision Medicine to Neurogenerative Diseases
Adam L. Boxer answers questions about the potential of "basket trials" to accelerate drug development for dementia and neurodegenerative disease.

-
Anticoagulant Benefits for Atrial Fibrillation Decrease With Age
The net clinical benefit of anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation decreases with age.

-
Silicon Valley takes on 'Dopamine Fasting 2.0' to battle bad habits, addiction