University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSF-
-
Juul Hits Deliver More Nicotine Than Cigarettes, Study Finds
-
How a Study of Horseshoe Crabs Led to Safer Joint Replacements
The breakthroughs came as Jack Levin was trying to find out if the cells normally circulating in the horseshoe crab’s blood, called amebocytes, triggered clotting, as platelets do in human blood.

-
JUUL Delivers Substantially More Nicotine than Previous Generation E-Cigs and Cigarettes
JUUL delivers substantially more nicotine to the blood per puff than cigarettes or previous-generation e-cigarettes and impairs blood vessel function comparable to cigarette smoke

-
Young Women Still May Be Getting Unnecessary Pelvic Exams
Pelvic examinations and cervical cancer screenings are no longer recommended for most females under age 21, but a new study has found that millions of young women are unnecessarily undergoing the tests.

-
Bay Area doctors target health consequences of childhood trauma
-
Brain Organoids Reveal Glioblastoma Origins
UCSF postdoctoral researcher for the first time succeeded in keeping a diverse array of glioblastomas alive in the lab using brain organoids
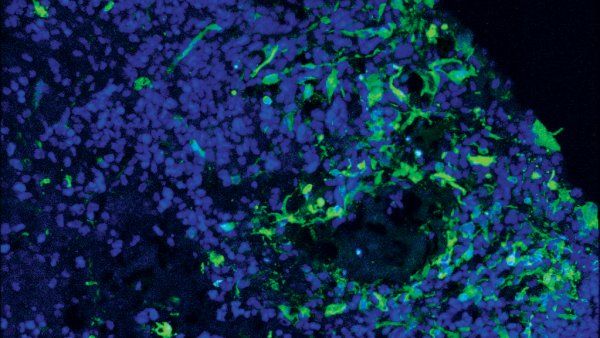
-
How Scientists Might Tame Cancer
Basic scientist Zena Werb, who has studied cancer cells in UCSF labs for more than four decades, shares her take on the future of cancer medicine.

-
Can Technology Mend Our Broken Minds
Scientists have documented the influence of information overload on attention, perception, memory, decision-making, and emotional regulation. But the same technologies contributing to the cognition crisis could help solve it, argues neuroscientist Adam Gazzaley.

-
The End of Infertility Is in Sight
Advances in medicine and public health have dramatically extended the lifespan of hearts, lungs, and other vital organs. But for women, the ovaries remain a stubborn exception. That may soon change, says fertility expert Marcelle Cedars.
-
Aging Is Not Optional. Or Is It?
With the global population of seniors projected to reach 1.5 billion by 2050, it will be more important than ever to reduce the burden of age-related disease. In the future, science will allow us to intervene in the aging process to make this a reality, according to geriatrician John Newman.

-
Study Might Point Alzheimer's Research in Whole New Direction
-
Who Will Benefit From Precision Medicine?
A future in which precision medicine benefits everyone is not guaranteed. For that to happen, UCSF experts argue, the health care industry must first tackle today’s health disparities, including differences in disease outcomes and access to care based on race, gender, and socioeconomic status.

-
Alzheimer ‘Tau’ Protein Far Surpasses Amyloid in Predicting Toll on Brain Tissue
Brain imaging of pathological tau-protein reliably predicts the location of future brain atrophy in Alzheimer’s patients a year or more in advance.
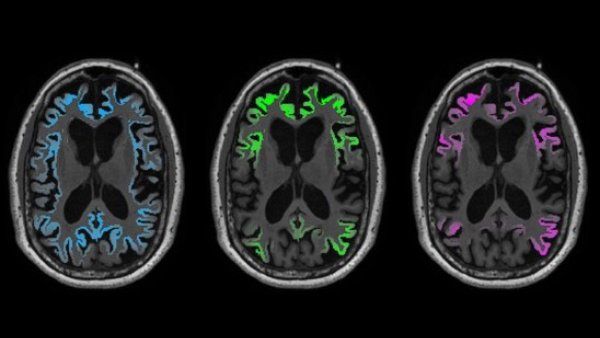
-
Pharmacies Leave Customers Hanging When It Comes to Disposing of Antibiotics and Opioids
A survey found that fewer than half of California pharmacies provided antibiotics and opioids disposal instructions meeting U.S. FDA guidelines, and just 10 percent followed the FDA’s preferred recommendation to take back unused medications from their customers.

-
The severe health effects of family separations at the US-Mexico border
-
Make 2020 the Year of Less Sugar
-
Mothers, Babies Overlooked in the Drug Crisis
-
Barring Nonmedical Exemptions Increases Vaccination Rates, Study Finds
The first rigorously controlled study of a 2016 California law that aimed to increase childhood vaccination rates by eliminating nonmedical exemptions has found the law worked as intended.
-
Bay Area Patients Stung By Unapproved Stem Cell Treatments As FDA Looks To Clamp Down
-
Should You Take a Direct-to-Consumer DNA Test?
With the rise of “direct-to-consumer” DNA tests, investigating your genes is easier than ever. But taking one of these tests may not be right for you, says UCSF professor Kathryn Phillips, PhD, who studies new health care technologies.

-
Old Drug Offers New Hope for Children with Devastating Disorder
A drug that once helped obese adults lose weight, but was withdrawn from the market due to heart risks, may be safe and effective for children with a life-threatening seizure disorder called Dravet syndrome.

-
E-cigarettes found to increase risk of chronic lung diseases
-
UCSF’s 11 Most Popular Health and Science Stories of 2019
Browse the stories that most engaged our readers in 2019.
-
E-Cigarettes Significantly Raise Risk of Chronic Lung Disease, First Long-Term Study Finds
E-cigarette use significantly increases a person’s risk of developing chronic lung diseases like asthma, bronchitis, emphysema or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, according to new UC San Francisco research, the first longitudinal study linking e-cigarettes to respiratory illness in a sample representative of the entire U.S. adult population.

-
In Childhood Cancer, Private Insurance Means Better Survival
Children and young adults with pediatric cancer are less likely to be alive five and 10 years following diagnosis if their health insurance is public, compared to those with private insurance.

-
New Study Says Mixing Alcohol & Drugs is a Dangerous Combination
-
UCSF donors’ experience with memory loss inspires funding of new clinic
-
UC Researchers Advise Healthy California for All Commission
Researchers at the University of California will serve as expert policy guides for the Healthy California for All Commission, which has been charged by the governor and state legislature with developing a path toward universal health coverage in California, including a possible single payer system.

-
Problem Drinkers Have Higher ‘Benzo’ Use, UCSF-Kaiser Permanente Study Shows
Problem drinkers are more likely than teetotalers and moderate drinkers to take benzodiazepines. When taken by heavier drinkers, benzodiazepines may heighten the risk for overdoses and accidents as well as exacerbate psychiatric conditions.
