Estrogen and Progesterone Stimulate the Body to Make Opioids
A new study found that female hormones can suppress pain signals before they reach the brain by making immune cells near the spinal cord produce opioids.

University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSFA new study found that female hormones can suppress pain signals before they reach the brain by making immune cells near the spinal cord produce opioids.

A Q&A w/Alison Cohen, PhD, MPH, who is among the estimated 5% of the population with Long COVID. She talks through the implications of Long COVID, and how she applies her scientific and personal experience to research this debilitating condition.

COPA syndrome causes lung hemorrhaging starting in childhood. But one in three people with the disease mutation are spared. UCSF scientists have discovered how a separate gene variant protects those relatives – lighting the way to a possible cure.
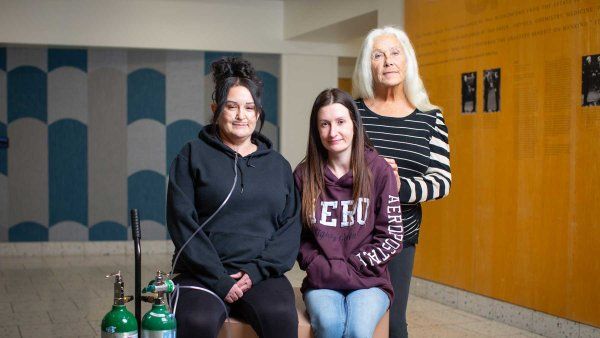
UCSF scientists have found that some cancers, like brain cancer, make unique, jumbled proteins that make them stand out. These newly recognized cancer-specific proteins, or antigens, could speed the development of potent immunotherapies that recognize and attack hard-to-treat tumors.
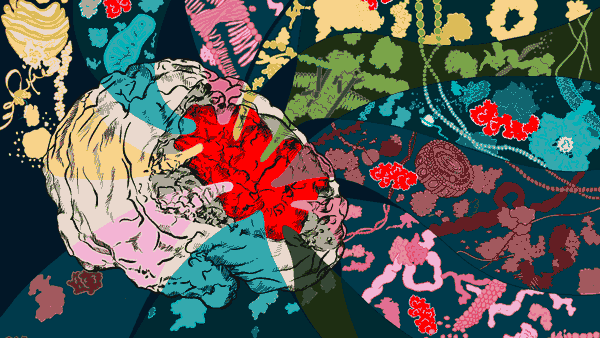
Scientists discover how cells in the uterus keep track of pregnancy to ensure an on-time delivery.
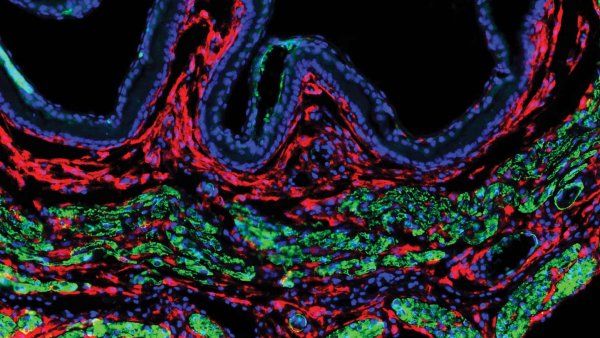
UCSF scientists developed a way to deliver radiation just to cancerous cells, rather than attacking both cancerous and healthy tissue. The therapy combines a drug to mark the cancer cells for destruction and a radioactive antibody to kill them.
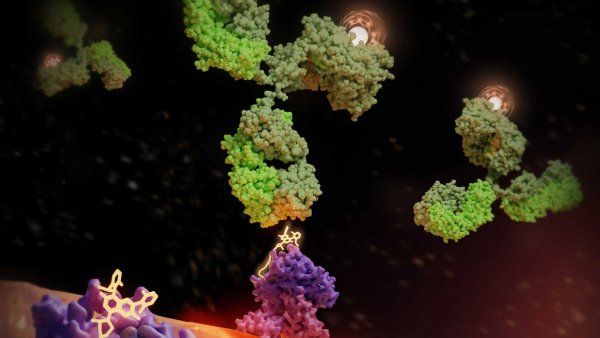
A new technology uses engineered T cells that act as immune “referees” to soothe overreacting immune responses. They also can mop up inflammatory molecules without lowering the entire body’s immune shields.

Nearly 50 UCSF researchers have been named to Clarivate’s list of most influential scientists for 2024.

UCSF researchers develop customizable SNIPR sensors that activate engineered cells only near tumors, promising precise cancer therapies with minimal side effects.
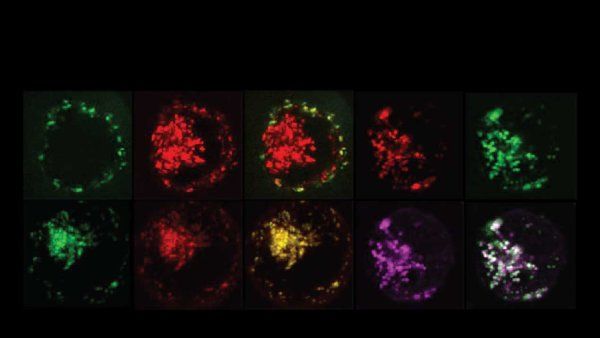
In June, UCSF treated its first patient with E-SYNC, its first homegrown CAR-T therapy, one of the first to show promise in treating certain types of brain cancers. This story builds on previous coverage to provide an overview of CAR-T therapy, accessibility and future horizons of applications in cancer and other illnesses like HIV.

A study shows how the keto diet affects the microbiome in ways that may reduce autoimmune responses in the gut.
Oral health has long been siloed from the rest of a person's health. But increasingly, researchers and clinicians, including those at UCSF, are finding ties between a person's oral health and their overall health.
UCSF officially broke ground on the Barbara and Gerson Bakar Research and Academic Building on Sept. 28, which will house state-of-the-art research facilities, and will also serve as the new home for the UCSF School of Nursing.

Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths in the U.S. and worldwide, pointing to the continuing need to improve treatment strategies and therapies that better patient survival and

An extra-long summer surge driven by new variants has prompted the early release of updated COVID-19 vaccines. A UCSF expert tells us what new vaccines could mean for the summer surge, who should get vaccinated, and when/where to get your vaccines.
Seth Blumberg, MD, PhD, explains the viral disease mpox, and what the recent emergency declaration from the World Health Organization means for us.
A study determines that a life-saving, inexpensive antibiotic, azithromycin, must be given to all children up to 5 years old in Sub-Sharan Africa to realize its full potential.

Face masks remain crucial in preventing the spread of COVID-19, even with vaccine availability. The decision to wear masks depends on vaccination status, risk factors, and local hospitalizations. Medical N95, KN95, or KF94 masks offer the best protection.

Researchers Micheal Peluso and Valerie Flaherman answer questions about what we know about one of COVID’s most enduring mysteries, including how to potentially reduce your risk and who is most likely to develop long COVID.
Adverse symptoms from the COVID-19 vaccine such as chills and headaches are linked to a robust antibody response, indicating increased efficacy compared with recipients who did not experience side effects.

Liver samples that spent two months in the International Space Station will be studied to observe how microgravity ages liver cells and impacts their ability to regenerate. Understanding how aging damages the liver – and ways to potentially reverse that damage – could pave the way for better prevention and treatment of liver disease.
